The World's Most Secure Messaging
Ultimate security: SimpleX network uses the most secure end-to-end encryption, with continuous post-quantum key exchange to protect all messages and metadata.
Unique privacy: SimpleX network has no user profile IDs, not even random numbers or keys. It provides better privacy of your contacts, protecting who you talk with from network servers.
No spam: nobody can contact you unless you share 1-time link or long-term address.
Data ownership: only your device stores your profiles, contacts and messages. You can securely move your data to another device. Servers store encrypted messages only while your device is offline.
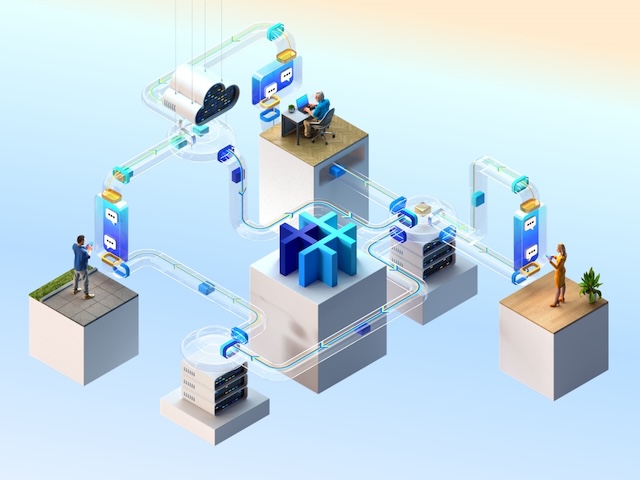
Secure decentralization: you control which servers to connect to. For security 4 different servers are used in each chat — they can't observe which IP addresses talk to each other.
How to connect to others
- Tap new chat button in the corner, then create 1-time link.
- Share the link with your contact via any other messenger or email - it is secure.
- Ask your contact to use the link in the app - click it after the app is installed or paste into the search field in the app.